Continuing on the series….
Here are few ways in which AR can be applied in a school dynamic.
- STUDENT ENGAGEMENT
Technology has often been cited as a tool to increase student engagement. Bonascio (2017) and Magana, Serrano & Rebello (2019) theorise that AR is able to prolong attention and focus, as when multimodal resources and haptic devices are used, higher levels of enjoyment are experienced. This gratification is significantly reduced in students that do not comprehend the mechanics of the technology and indicated that whilst utilising AR can improve digital literacy, explicit teaching is required to ensure that all students are able to interact successfully with the technology (Magana, Serrano & Rebello, 2019).
2. INQUIRY LEARNING
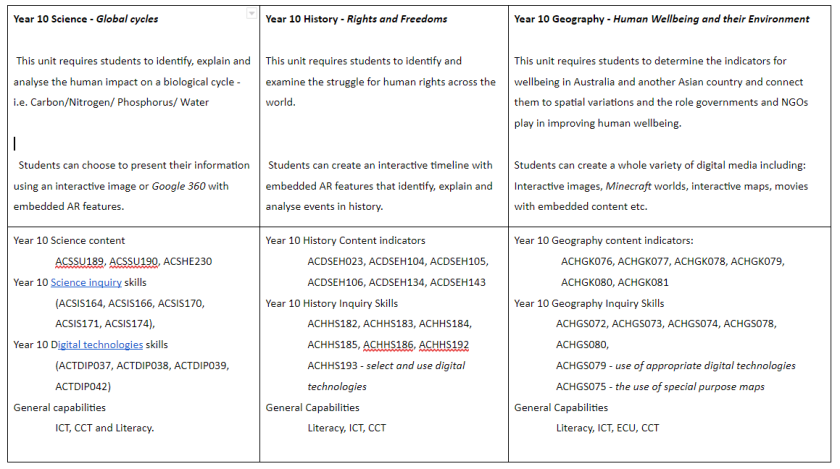
Oddone (2019) and Foote (2018) both suggest that greater educational benefits arise from students creating their own interactive images and overlays rather than using supplied ones. Apps such as Metaverse or Augment can be used by students to construct their own interactive content and would be an ideal cross curricular inquiry task across any discipline, but have curriculum value within the Science, History and Geography inquiry skills section. Examples of inquiry tasks include:
3. ABSTRACT CONCEPTS & STEM SUBJECTS
Magana, Serrano & Rebello (2018, p.526) believe that there is a positive effect to using multimodal resources and active learning for science and its related fields. This is because students often need assistance with visualising complex and abstract concepts (Saidin, Abd Hali & Yahaya, 2015; Riva, Banos, Botella, Mantovani & Gaggioli, 2016). Abstract concepts can be problematic for many students because of the difficulty students can have in visualising theoretical postulations (Furio, Fleck, Bousquet, Guillet, Canioni & Hachet, 2017, p.2-3 ). This struggle can negatively influence a student’s perception of the content material and lead to adverse learning outcomes (Furio et al., 2017, p.2-3 ). AR technology allows students to visualise the concept, albeit in animation, and increase comprehension which leads to improved outcomes (Saidin, Abd Hali & Yahaya, 2015, Wu et al., 2013). This is because haptic devices allow students to manipulate and utilise their sensory faculties when they are constructing knowledge. Large and small phenomena, as well as anatomical figures, can be visualised using AR technology (Wu et al. 2013).
High school curriculum linked examples include:
4. READING – RECREATIONAL & INFORMATIONAL
AR books is the largest growing trend in children’s publishing and that many publishers are supplementing traditional texts with AR embedded resources (Levski, 2018; Zak, 2014). This is because AR books are seen as more innovative and able to improve flagging reading rates in children and adolescents (Levski ,2018, Zak, 2014). Many young readers find the interactivity extremely engaging and the use of technology appeals to digital natives (Magana, Serrano & Rebello, 2019).
5. LITERACY
Mayahayuddin & Mamat, (2019) point out that the multimodal nature of AR improves literacy because the audio visual cues assist students in decoding. Additionally, AR enables students that have low focus or attention to enhance their learning as it grants access to language in both formal and informal contexts, which is very useful for students with ADD, ADHD and those with social anxiety (Rafiq & Hashim, 2018, p.31; Mayayuddin & Mamat, 2019. These benefits are further improved when AR is combined with gaming principles which provides additional interest and intrinsic motivation (Mayahayuddin & Mamat, 2019; Levski 2018).
REFERENCES
Foote, C. (2018). Is it real or is it VR? Exploring AR and VR tools. Computers in Libraries. Retrieved from http://web.b.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.csu.edu.au/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=0&sid=6093ea4d-06fa-42b1-8400-75e5bd1dd875%40pdc-v-sessmgr03
Furio, D., Fleck, S., Bousquet, B., Guillet, JP., Canioni, L., & Hachet, M. (2017). HOBIT: Hybrid optical bench for innovative teaching. CHI’17 – Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. Retrieved from https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01455510/file/HOBIT_CHI2017_authors.pdf
Levski, Y. (2018). 10 Augmented Reality Books That Will Blow Your Kid’s Mind. AppReal- VR [Blog]. Retrieved from https://appreal-vr.com/blog/10-best-augmented-reality-books/
Mahayuddin, Z., & Mamat, Z. (2019). Implementing augmented reality (AR) on phonics based literacy among children with autism. International Journal on Advanced Science Engineering Information Technology 9 (6). Retrieved from https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/296918932.pdf
Oddone, K. (2019). Even better than the real thing? Virtual and augmented reality in the school library. SCIS Connections. (110). Retrieved from https://www.scisdata.com/media/1921/scis-connections-110.pdf
Saidin, N. Abd Halim, N., & Yahaya, N. (2015). A review of research on augmented reality in education: Advantages and applications. International Education Studies, 8(13). Retrieved from http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.730.8456&rep=rep1&type=pd
Rafiq, K., & Hashim, H. (2018) Augmented reality game (ARG), 21st century skills and ESL classroom. Journal o fEducational and Learning Studies. 1 (1) pp29-34. Retrieved from https://journal.redwhitepress.com/index.php/jels/article/view/23/pdf
Riva, G., Banos, R., Botella, C., Mantovani, F., & Gaggioli, A. (2016). Transforming experience: The potential of augmented reality and virtual reality for enhancing personal and clinical change. Frontiers in Psychiatry 7. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5043228/pdf/fpsyt-07-00164.pdf
Wu, H., Lee, S., Chang, H., & Liang, J. (2013). Current status, opportunities and challenges of augmented reality in education. Computers & Education, 62. Pp41-49. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2012.10.024
Zak, E. (2014). Do you believe in magic? Exploring the conceptualisation of augmented reality and its implication for the user in the field of library and information science. Information Technology and Libraries.